Supersonic flow hitting a rectangular obstacle
Case directory
$FOAM_TUTORIALS/compressible/rhoCentralFoam/forwardStep
Summary
A virtual non-viscous gas flow, "normalized" to have a sound velocity of 1 m/s at a temperature of 1 K, hitting an obstacle at supersonic speed is calculated for 4 seconds.
The gas flows in from the region "inlet" at 3 m/s (Mach number 3) and out from the region "outlet". The region "top" and "bottom" are symmetric boundaries, and the region "obstacle" is a slip wall.
 Model geometry
Model geometry
The turbulence model is not used, and the analysis is performed in 2-dimensions.
The physical properties of the gas are specified in the file constant/thermophysicalProperties as follows.
mixture
{
specie
{
nMoles 1;
molWeight 11640.3;
}
thermodynamics
{
Cp 2.5;
Hf 0;
}
transport
{
mu 0;
Pr 1;
}
}
The meshes are as follows, and the number of mesh is 16128.
 Meshes
Meshes
The calculation result is as follows.
The flow velocity is as follows.
 Flow velocity at 0.5 sec (U)
Flow velocity at 0.5 sec (U)
 Flow velocity at 2.5 sec (U)
Flow velocity at 2.5 sec (U)
 Flow velocity at 4 sec (U)
Flow velocity at 4 sec (U)
And the pressure is as follows.
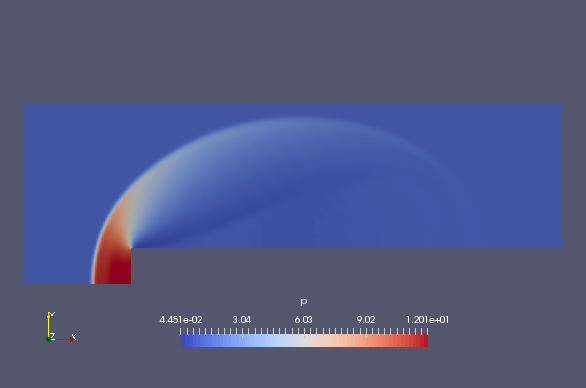 Pressure at 0.5 sec (p)
Pressure at 0.5 sec (p)
 Pressure at 2.5 sec (p)
Pressure at 2.5 sec (p)
 Pressure at 4 sec (p)
Pressure at 4 sec (p)
Note that the upper region of the computational domain, "top", is a symmetric boundary.
Commands
cd forwardStep
blockMesh
rhoCentralFoam
paraFoam
Calculation time
105.64 seconds *Single, Inter(R) Core(TM) i7-8700 CPU @ 3.20GHz 3.19GHz